Sha256 = Secure ?
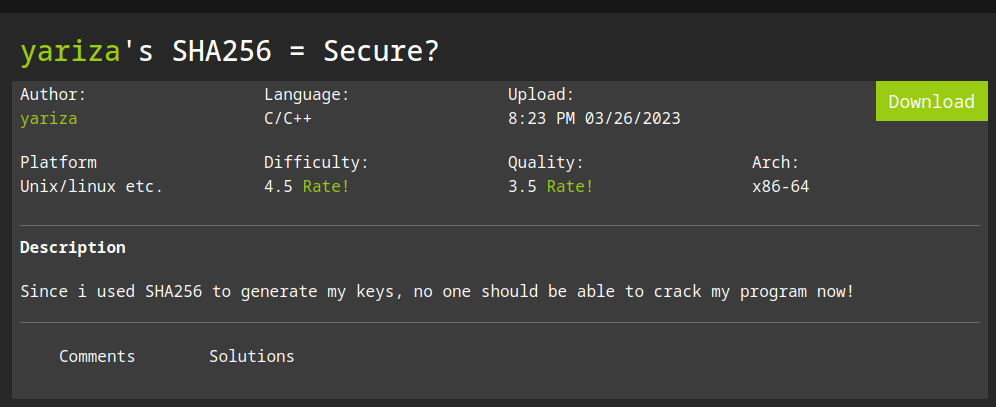
This a challenge about the hashing algorithm called Sha256 link to challenge here, today we are going to reverse the logic implementation.
A zip file was given in the site downloading and extracting we have:
we could see that the executable is a linux x86-64 non-striped binary, executing the file we have :
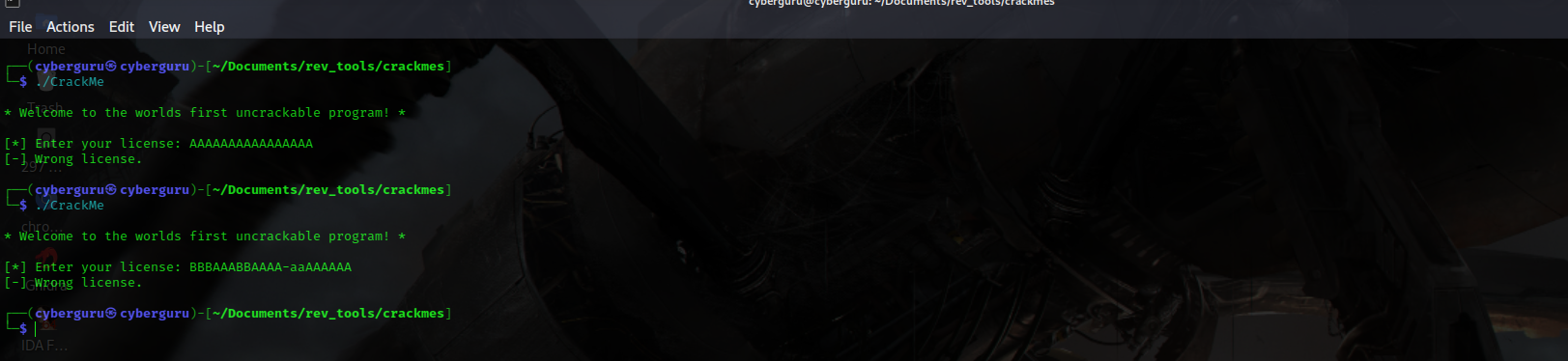
the program prompt us for a license key, plugging the program to Ghidra and decompiling the binary we have :
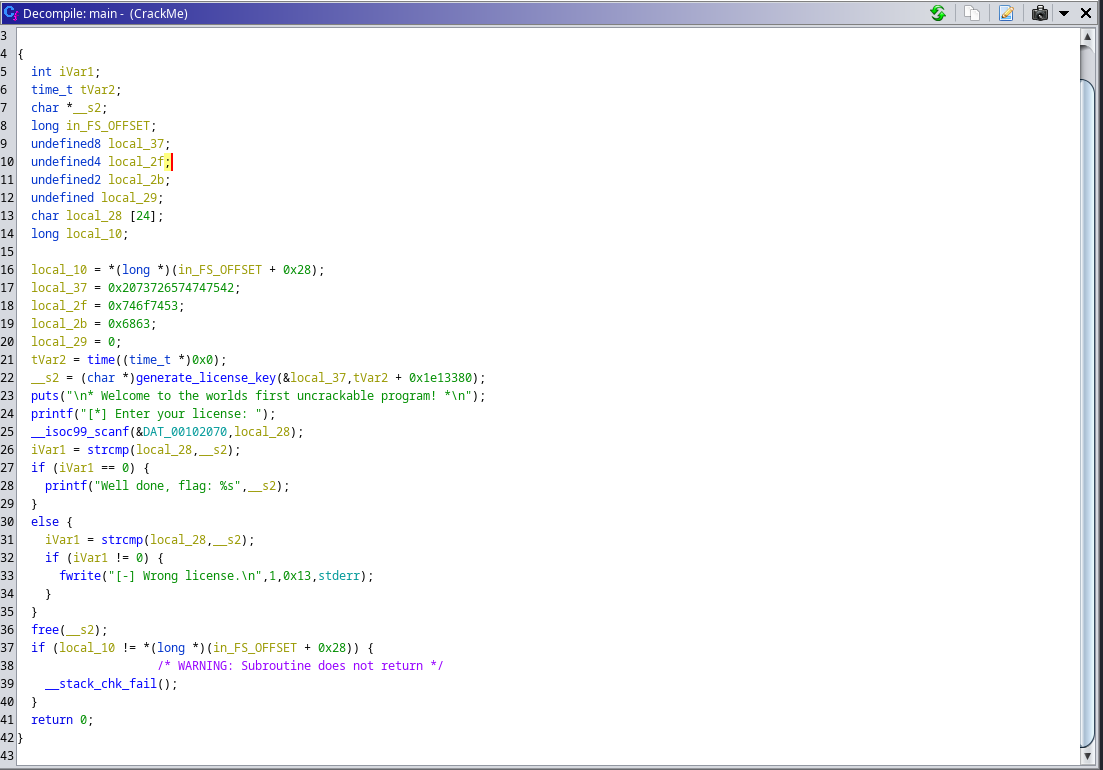
we could see that the program start execution from main function which performs:
-
The initialization of variables and structures:
iVar1: An integer variable. tVar2: A time_t variable. __s2: A character pointer. in_FS_OFFSET: A long variable used for stack checking. local_37, local_2f, local_2b, local_29: Variables used to store values of different data types. local_28: A character array used to store user input. local_10: A long variable used for stack checking.
-
It assigns values to
local_37,local_2f,local_2b, andlocal_29to represent parts of a license key. -
It gets the current time using time and adds an offset to it, storing the result in tVar2.
-
It calls the generate_license_key function with the address of
local_37andtVar2 + 0x1e13380as parameters to generate a license key. The resulting license key is assigned to __s2. -
It displays a welcome message.
-
It prompts the user to enter a license key.
-
It reads the user input using
scanfand stores it inlocal_28. -
It compares
local_28with the generated license key stored in__s2usingstrcmp. -
If the comparison result is equal to 0, it means the entered license key matches the generated license key. It prints a success message along with the flag (the generated license key).
-
If the comparison result is not equal to 0, it means the entered license key does not match the generated license key. It prints an error message.
-
It frees the memory allocated for the license key using free.
-
It performs stack checking by comparing local_10 with the value at the address *(long *)(in_FS_OFFSET + 0x28). If they are not equal, it indicates a stack overflow and triggers a failure.
One important thing to note from the function, is that the parameters that is passed to the generate_licenses function is time dependent, so each time the program is runned, the license key changes with this constraint in mind we could choose to write a script that generates the license key for the next 5 seconds and plug each one into the program till we get the correct one or use a debugger to get the content that is returned and stored in memory when the generate_licenses function is executed. Well let’s go with the easier approach that’s the latter.
Before going into the debugger what’s really going on in the generate_licenses_key function let’s check it out:
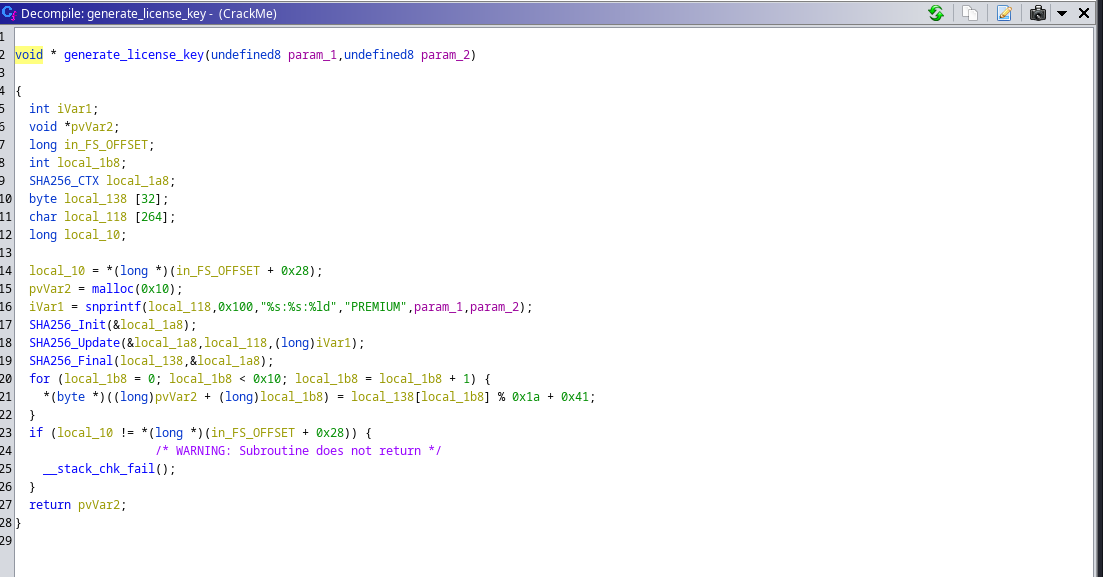
from the above pic we could see that :
-
It allocates memory for the license key using
malloc(0x10)(16 bytes) and assigns the pointer topvVar2. -
It formats a string using
snprintfand stores it in local_118. The string is formatted as “PREMIUM:param_1:param_2”, whereparam_1andparam_2are the input parameters passed to the function. -
It initializes the
SHA256_CTXstructurelocal_1a8usingSHA256_Init. -
It updates the
SHA256_CTXstructurelocal_1a8with the content oflocal_118usingSHA256_Update. -
It finalizes the SHA-256 hashing operation and stores the resulting hash in
local_138usingSHA256_Final. -
It loops through each byte of
local_138, performs a modulo operation (%) with0x1a (26)and adds0x41(65) to the result. This operation converts the byte value into a character between ‘A’ and ‘P’. The resulting characters are stored in the memory pointed to by pvVar2, generating the license key. -
Finally, it performs stack checking by comparing
local_10with the value at the address*(long *)(in_FS_OFFSET + 0x28).If they are not equal, it indicates a stack overflow and triggers a failure. -
The function returns the generated license key stored in
pvVar2which is our main target here
Going into GDB debugger with the program:
from the assembly we could identify where the returned license key is stored in the heap memory which is at:
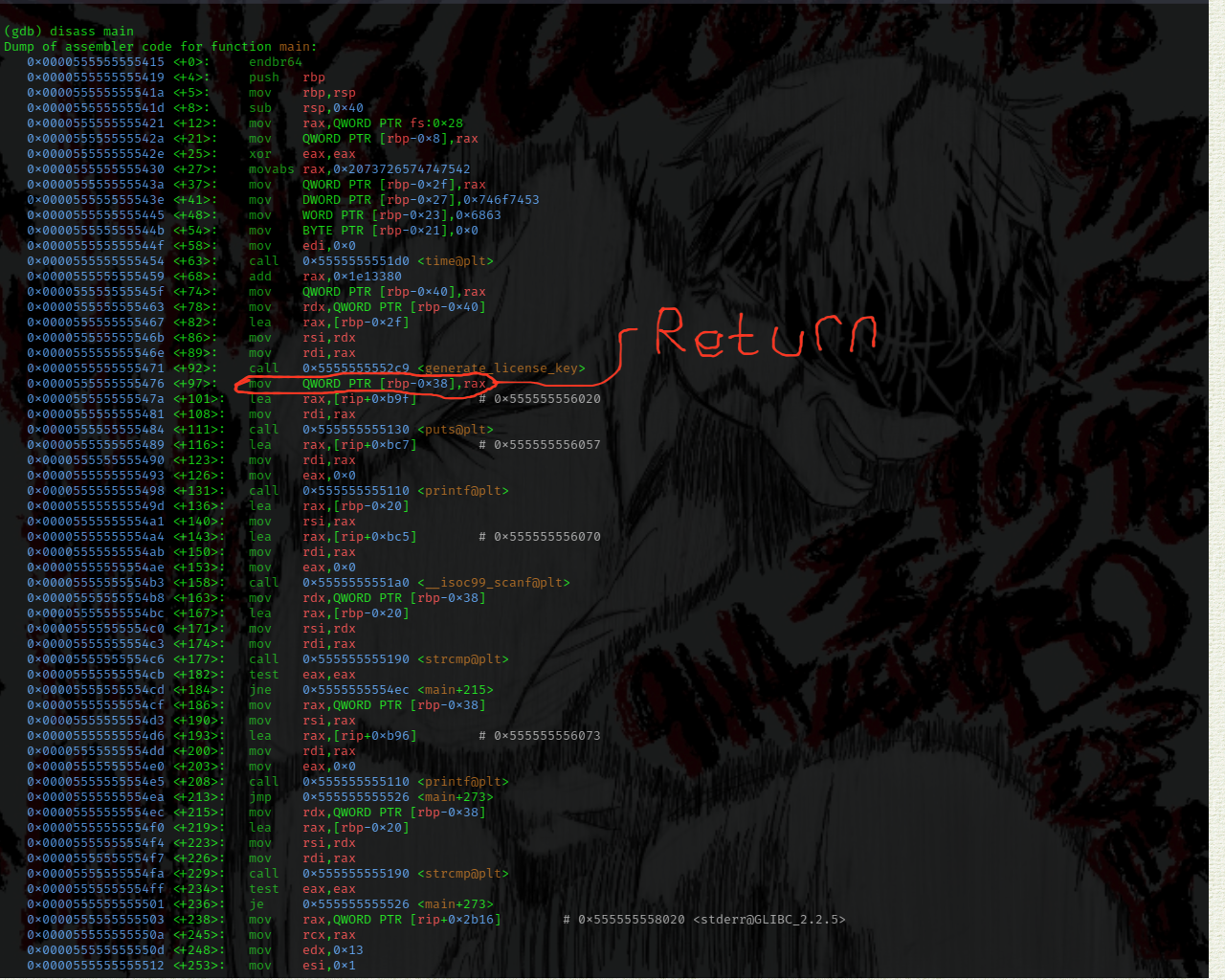
Setting a breakpoint at that line and running the program we hit the breakpoint, printing the content of the rax register reveals us our license key, submitting it to the program gives us our flag!!!!!!!!
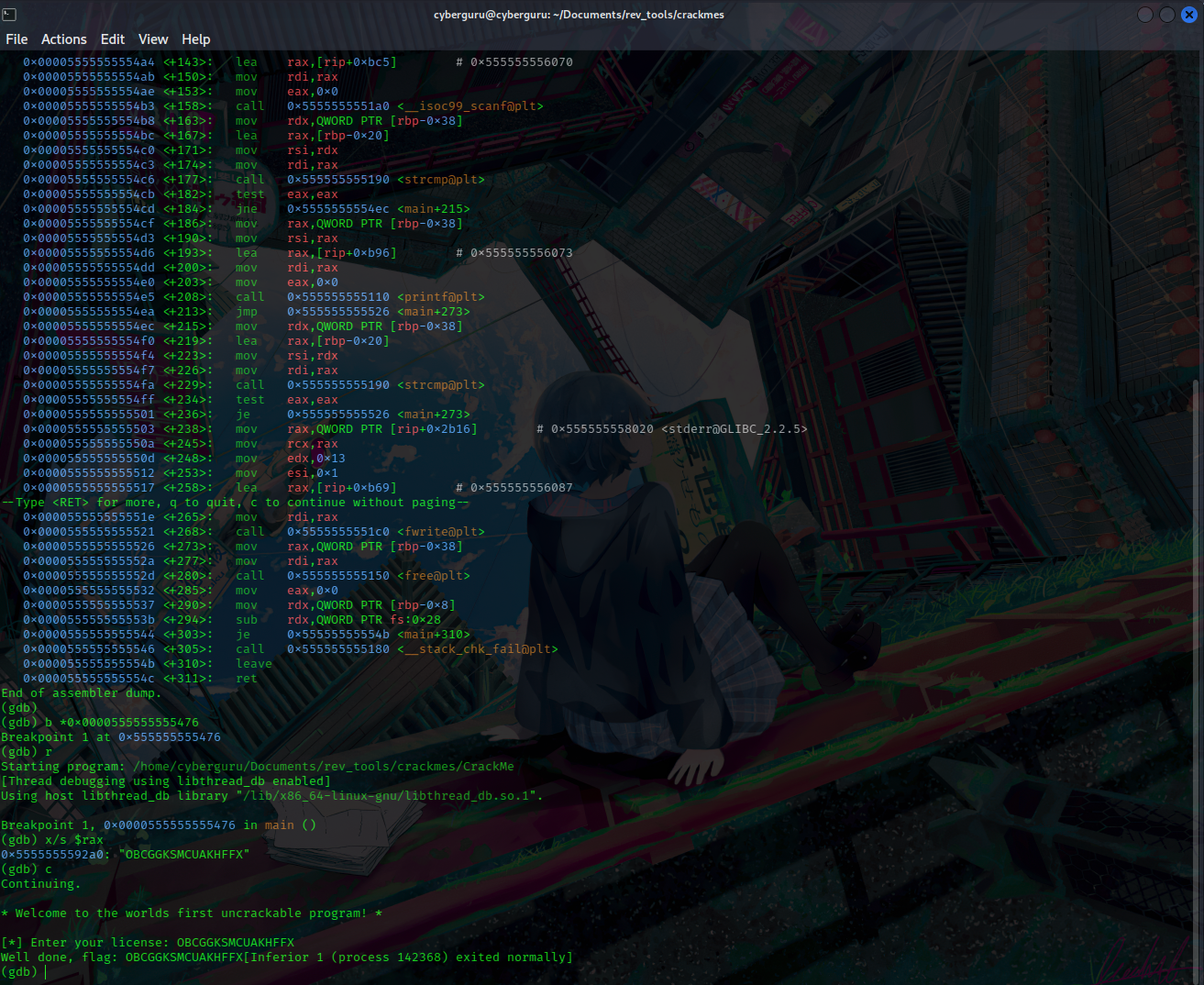
But in this case our flag is not constant, it’s time Dependent(i.e it varies with time)